How Fuel Injectors Work and Their Role in Combustion Efficiency
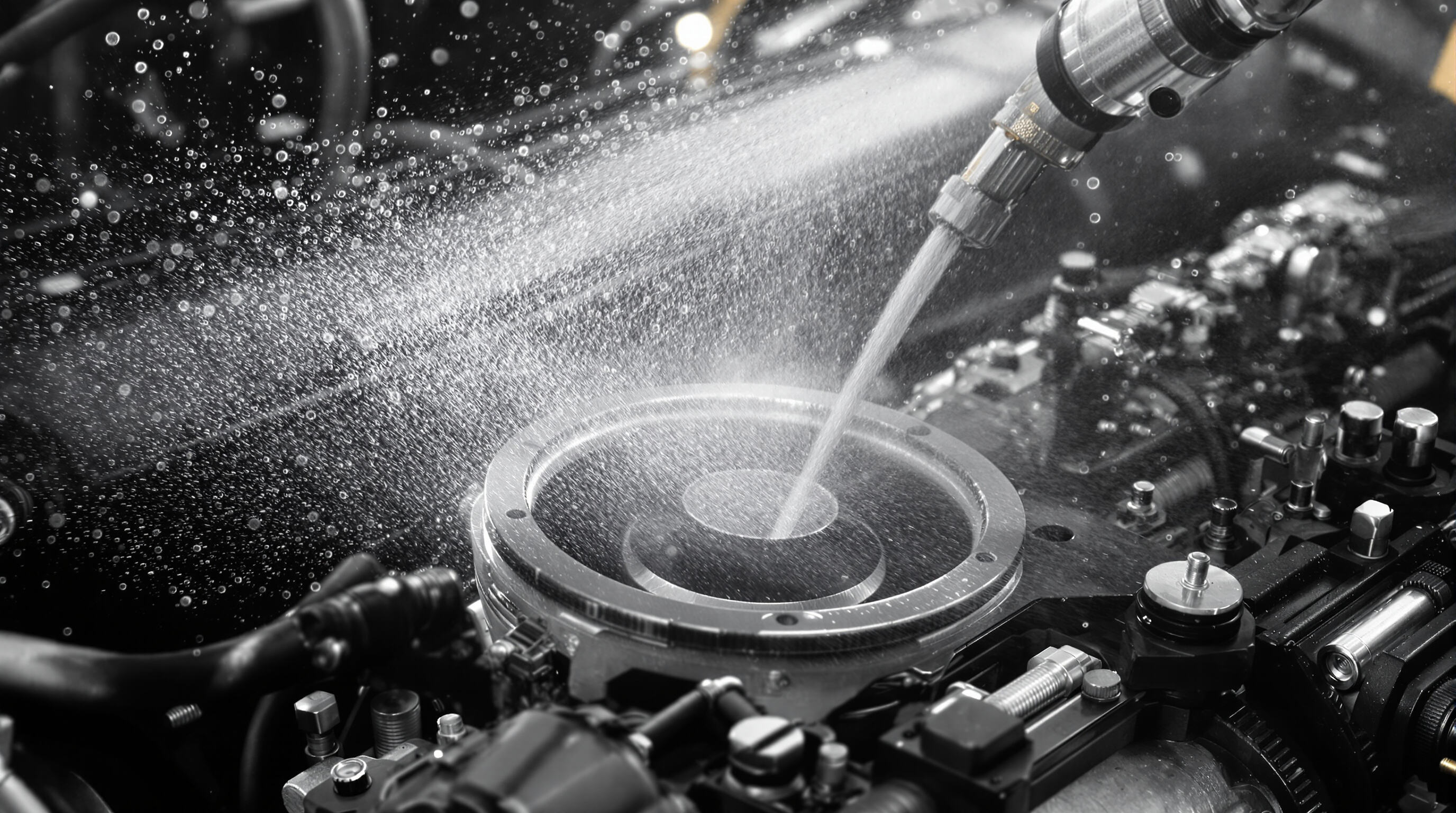

Basic Operation of Fuel Injectors in Modern Engines
Fuel injectors work like really accurate valves that get their instructions from the engine control unit, or ECU for short. They actually shoot tiny droplets of fuel right into those intake ports or straight into the combustion chamber itself. What makes them so good is how different they are from old school carburetors. These modern injectors can tweak how much fuel comes out and what shape it takes hundreds of times every second. They do this based on information coming in about things like engine speed, how hard the car is working, and even temperature changes. Because of this constant adjusting, cars run better no matter what kind of driving someone does. Performance stays strong while getting better gas mileage too.
Injection Pressure and Precision in Fuel Delivery
High-pressure systems in direct-injection engines operate between 1,500 and 3,000 PSI, forcing fuel through micron-scale nozzles to create droplets 5-10 times smaller than a human hair. Multi-hole injectors distribute fuel more evenly than single-hole designs, reducing localized rich or lean zones by 18-22% and improving combustion consistency.
Fuel Atomization and Its Impact on Combustion Efficiency
Fine fuel atomization reduces unburned hydrocarbon emissions by 30% and increases thermal efficiency by 8-12% (SAE International, 2022). Smaller droplets vaporize faster, creating a more homogeneous air-fuel mixture that supports lean-burn strategies-particularly effective during partial-load operation to minimize fuel waste.
Optimizing Air-Fuel Mixture Through Precise Injector Timing
Injector timing accuracy within 1-2 of crank angle rotation prevents detonation in turbocharged engines. Sequential injection, tailored to individual cylinder airflow, maintains air-fuel ratios within ±0.03 of lambda 1.0 under 95% of operating conditions, ensuring stable combustion and peak efficiency.
Direct vs. Port Fuel Injection: Efficiency Comparison and Trade-offs
How direct fuel injection (DFI) enhances fuel efficiency
Direct fuel injection works by spraying fuel directly into the engine's combustion chamber under very high pressure, sometimes reaching around 3,000 psi. This results in much finer fuel atomization, about 20% better than what we see with port injection systems. The improved atomization lets engines run with higher compression ratios too. While traditional port injection typically maxes out at around 10:1 compression, direct injection can handle up to 12:1. According to recent research from 2024 on combustion efficiency, this setup also cuts down on wasted unburned fuel by somewhere between 9% and 15%. And when manufacturers combine direct fuel injection with turbochargers, the fuel savings get even better. Tests conducted by the EPA show these combined systems improve fuel economy by approximately 11% to 18% across standard testing cycles.
Port fuel injection (PFI) efficiency and reliability benefits
PFI systems offer superior long-term reliability, maintaining 97.8% component functionality over 100,000 miles-significantly higher than DFIs 89.3% (SAE International, 2023). The fuels path across intake valves provides a cleaning effect, preventing 83% of carbon buildup that plagues DFI engines and preserving airflow without requiring specialized maintenance.
Performance and emissions: DFI vs. PFI real-world implications
DFI engines achieve 6-9% greater thermal efficiency during highway driving but emit 34% more ultrafine particulates (2.5 µm). In contrast, PFI maintains cleaner exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) pathways, reducing particulate emissions by 28%, though they deliver 7% less torque at low RPMs.
Industry paradox: Higher efficiency with DFI vs. increased particulate emissions
While DFI reduces CO emissions by 12% per kilometer, its stratified combustion modes generate 41% more PM2.5 particles than PFI. As global emissions standards tighten, automakers must add gasoline particulate filters-increasing production costs by $240-$390 per vehicle-to offset this drawback.
Clogged or Dirty Fuel Injectors: Effects on Fuel Economy and Performance
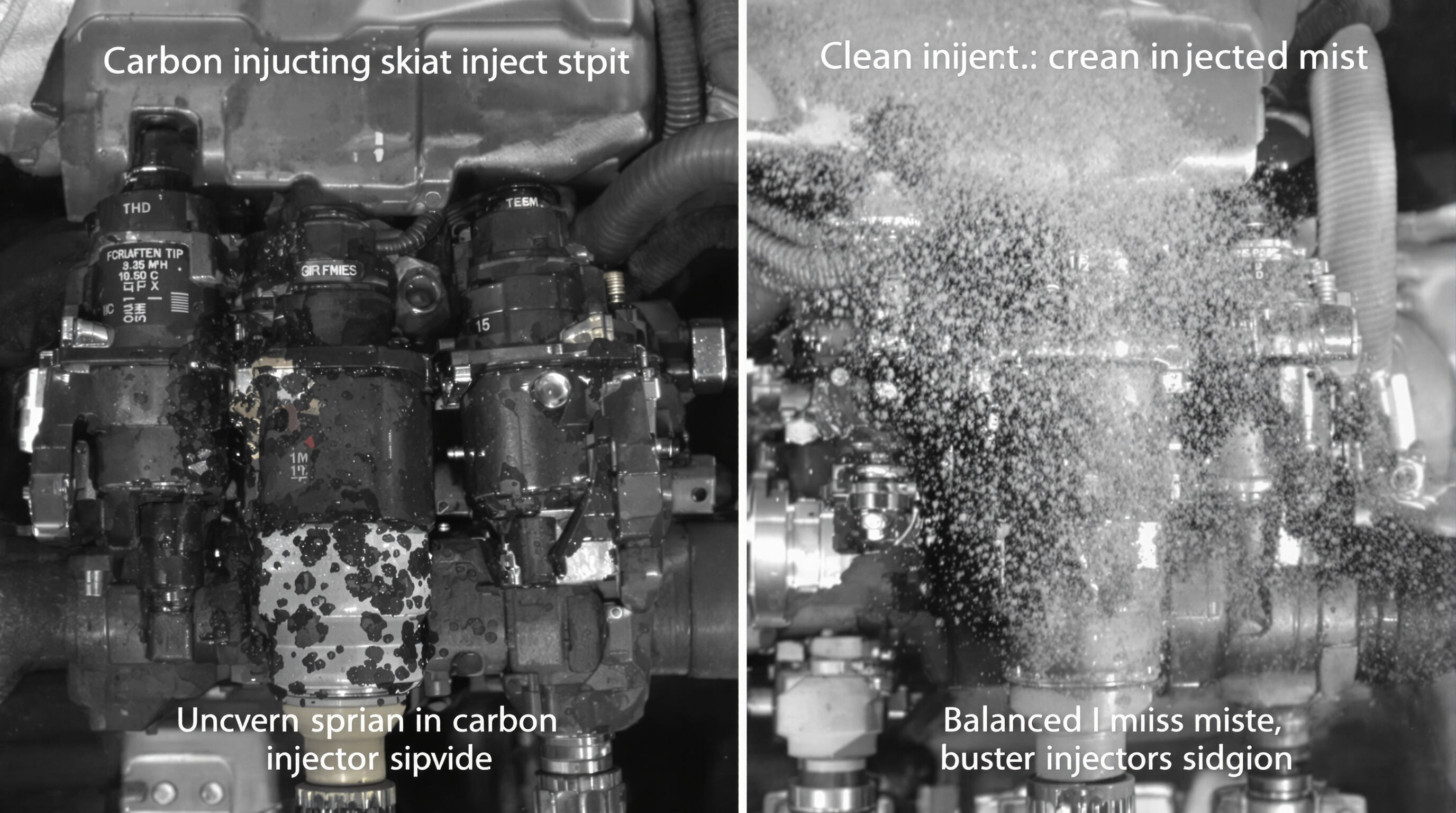
How Deposits Reduce Fuel Injector Efficiency and Disrupt Spray Patterns
Carbon deposits from low-quality fuel or contaminants can reduce injector flow capacity by up to 30% (Automotive Engineering Society, 2021). These blockages distort spray patterns, leading to uneven droplet formation instead of a fine mist. Poor atomization causes incomplete combustion, which alone can reduce fuel economy by 10-15% (Fleet Management Journal, 2022).
Symptoms of Faulty Injectors: Poor Mileage, Rough Idling, and Misfires
Clogged injectors typically cause three key issues:
- 12-15% drop in fuel efficiency due to over-fueling in response to poor combustion
- Rough idling or stalling from inconsistent fuel delivery at low RPMs
- Acceleration hesitations and misfires caused by lean air-fuel mixtures during throttle application
Impact of Clogged Injectors on Air-Fuel Balance and Engine Performance
| Condition | Fuel Delivery Issue | Combustion Result | Long-Term Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rich mixture | Over-fueling | Unburned fuel | Catalyst converter damage |
| Lean mixture | Under-fueling | Pre-ignition | Piston/valve wear |
Disrupted spray patterns force the ECU to oscillate between rich and lean corrections, increasing hydrocarbon emissions by 20-40% (Consumer Reports, 2021). This imbalance accelerates carbon buildup, worsening performance and shortening engine life if unaddressed.
Fuel Injector Maintenance for Optimal Fuel Efficiency
Benefits of Regular Fuel Injector Cleaning on Fuel Economy
Dirty injectors can degrade atomization by up to 58%, directly impairing combustion efficiency (SAE, 2023). Professional cleaning restores factory spray patterns, correcting flow issues that waste 6-12% of fuel. A 2024 Fleet Efficiency Study found vehicles with biennial maintenance achieved 4.2% better fuel economy than those without.
Common Maintenance Practices to Prevent Injector Clogging
- Use Top Tier® detergent gasoline to reduce deposit formation
- Replace fuel filters every 30,000 miles (per manufacturer guidelines)
- Avoid consistently running below one-quarter tank to minimize sediment intake
- Take weekly high-RPM highway drives (15+ minutes) to help clear minor deposits
Fuel Additives and Professional Cleaning: Do They Save Fuel?
Certified fuel injector cleaners reduce deposit buildup by 34-41% when used quarterly. While additives help maintain performance, professional hydrodynamic cleaning removes 89% of stubborn deposits unreachable by chemicals. The National Automotive Service Task Force recommends combining monthly additive use with bi-annual professional cleaning to sustain optimal fuel economy.
Does Replacing Fuel Injectors Improve Fuel Economy?
When Replacement Is Necessary: Worn or Failing Injectors
When fuel injectors start to degrade, they mess up the way fuel sprays into the engine and throw off the air-fuel mixture balance. This usually results in about a 10 to 15 percent drop in fuel efficiency because the fuel doesn't burn completely. Drivers often notice problems first through rough idling, hesitation when accelerating, or even engine misfires. These are clear signs that the injectors aren't performing within factory specifications anymore. At some point, simply cleaning them won't fix the issue, particularly for older cars past the 100,000 mile mark. After so many miles, the rubber seals begin to deteriorate and the electrical connections become sluggish from constant use. Replacement becomes necessary rather than just a good idea at this stage.
Case Study: Fuel Economy Gains After Injector Replacement in High-Mileage Vehicles
Looking at data from 47 vehicles with lots of mileage, we found that replacing fuel injectors improved fuel economy by about 12% on average. For cars with direct injection systems, horsepower came back somewhere between 8 to 14 units. Port injected engines saw better performance too, burning less fuel when starting up cold by around 5 to 9%. When mechanics installed new injectors that were correctly set up, they fixed the air fuel balance issue in almost 9 out of 10 cases according to Fleet Efficiency Report from last year. This cut down harmful hydrocarbons by nearly 20%. So what does all this mean? Regular maintenance like injector replacement really makes a difference for older engines struggling with efficiency problems.
FAQ
What is the main function of fuel injectors in a vehicle?
Fuel injectors accurately deliver fuel into the engine, ensuring the optimal air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion and improved vehicle performance.
What are the benefits of maintaining clean fuel injectors?
Maintaining clean fuel injectors ensures optimal fuel spray patterns, which enhance combustion efficiency, leading to better fuel economy and engine performance.
When should fuel injectors be replaced?
Fuel injectors should be replaced when they are worn or failing, usually noticeable through rough idling, acceleration hesitation, or misfires, particularly in older vehicles with over 100,000 miles.
Table of Contents
- How Fuel Injectors Work and Their Role in Combustion Efficiency
- Direct vs. Port Fuel Injection: Efficiency Comparison and Trade-offs
- Clogged or Dirty Fuel Injectors: Effects on Fuel Economy and Performance
- Fuel Injector Maintenance for Optimal Fuel Efficiency
- Does Replacing Fuel Injectors Improve Fuel Economy?
- FAQ
